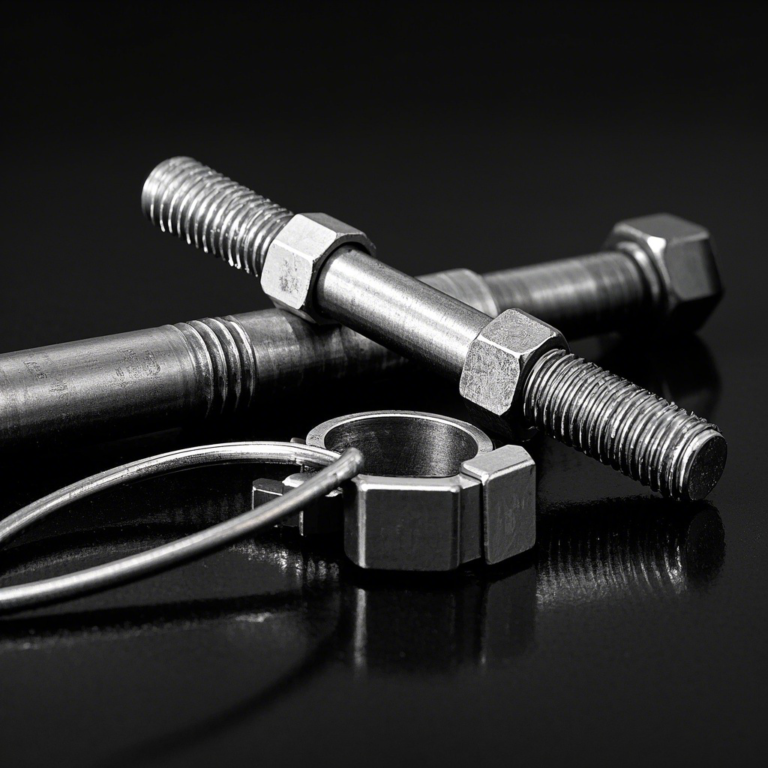
Hose clamps above water line and problem solving
1. What is the hose clamp above the waterline and what is its function? The hose clamp above the waterline,…
1. What is the hose clamp above the waterline and what is its function?
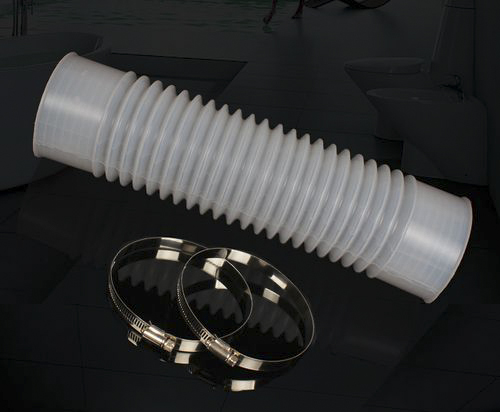
The hose clamp above the waterline, also called a clamp, is a mechanical part used to fasten the connection of waterline pipes and hoses. It is usually made of metal, and common types include worm drive hose clamps, spring hose clamps, etc. In the waterline system, the hose clamp is like a “guardian”, which fixes the pipe or hose tightly at the joint by applying pressure to prevent water from leaking from the interface under pressure, ensuring the stable and efficient operation of the waterline system. Whether it is a cooling water line in industrial production or a household water supply pipeline, the hose clamp is indispensable and is crucial to ensure the sealing and safety of the water system.

2. What problems are likely to occur with the hose clamp above the waterline?
1. Looseness problem: During the operation of the water line, the impact of water flow, the vibration of the pipeline, and the thermal expansion and contraction caused by the change of ambient temperature may gradually loosen the throat clamp. Once the throat clamp is loose, the sealing of the pipe connection will decrease, causing water leakage.
2. Corrosion problem: Since the throat clamp is in contact with water for a long time, if the material has poor corrosion resistance, it is easy to corrode. Especially in some water line environments with poor water quality or containing corrosive chemicals, the metal surface of the throat clamp will be oxidized and rusted, which will not only reduce the fastening ability of the throat clamp, but also cause the throat clamp to break in severe cases, causing water line leakage accidents.
3. Specification mismatch problem: If the selected throat clamp specification does not match the pipe or hose, an oversized throat clamp cannot provide sufficient fastening force, and an oversized throat clamp may damage the pipe or hose, which will also cause water leakage and other problems.
4. Wear problem: Frequent installation and disassembly, or improper operation during installation, may cause wear of the parts of the throat clamp. For example, after the worm and nut of a worm-driven throat clamp are twisted multiple times, the threads may wear out, resulting in an inability to tighten effectively, thus affecting the tightening effect of the throat clamp.
3. How to determine if there is a problem with the hose clamp above the waterline?
1. Observe for signs of water leakage: The most intuitive way to judge is to check whether there are water stains, dripping or water leakage at the connection of the waterline pipe. If water marks are found around the pipe interface and the pipe itself is ruled out of rupture, it is likely that there is a problem with the hose clamp.
2. Check the appearance of the hose clamp: Carefully check whether there is obvious corrosion or rust on the surface of the hose clamp, or whether the parts are damaged or deformed. For worm-driven hose clamps, check whether the worm and nut can rotate normally and whether the threads are worn.
3. Feel the tightness: While ensuring that the pressure of the waterline system is normal, gently shake the hose clamp at the pipe connection with your hand. If it feels loose, it means that the hose clamp may have lost its proper tightening force.
4. What are the solutions to different problems with throat clamps?
1. Loose hose clamp: First, turn off the water supply to the waterline system to release the pressure in the pipe. Then use a suitable tool, such as a screwdriver (for worm drive hose clamps) or pliers (for spring hose clamps) to retighten the hose clamp. During the tightening process, pay attention to uniform force to avoid over-tightening and damage to the pipe or hose. If the hose clamp is loose multiple times, it is recommended to replace it with a better quality and stronger tightening performance.
2. Corrosion of the hose clamp: For slightly corroded hose clamps, you can first remove it, sand off the rust on the surface with sandpaper, and then apply anti-rust paint or anti-rust grease before reinstalling it. If the hose clamp is severely corroded, broken or severely deformed, it must be replaced with a new one immediately. When choosing a new hose clamp, materials with good corrosion resistance, such as stainless steel hose clamps, should be given priority.
3. Specification mismatch: According to the actual size of the pipe or hose, choose a hose clamp of appropriate specifications for replacement. Before purchasing a hose clamp, accurately measure the outer diameter of the pipe and refer to the specification parameter table of the hose clamp to ensure that the new hose clamp can perfectly fit the pipe and provide a good tightening effect.
4. Wear of throat hoop: If the throat hoop parts are worn, the worn parts should be replaced in time. For some throat hoop parts that cannot be replaced individually, such as integral spring throat hoop, once the wear is serious, the entire throat hoop needs to be replaced. When installing a new throat hoop, pay attention to the correct operation method to avoid the throat hoop being worn again due to improper operation.
5. How to prevent problems with the hose clamps above the waterline?
1. Choose high-quality throat hoops: When purchasing throat hoops, choose products produced by regular manufacturers, and give priority to throat hoops with excellent materials and exquisite workmanship. For example, in a humid and corrosive environment, stainless steel or throat hoops with special anti-corrosion treatment should be selected.
2. Correctly install the throat hoops: When installing the throat hoops, ensure that the interface of the pipe or hose is clean and dry. The throat hoops should be installed in the appropriate position of the interface and the tightening force should be moderate. At the same time, follow the installation instructions of the throat hoops and use the correct tools and methods for installation.
3. Regular inspection and maintenance: Establish a system for regular inspection of waterline throat hoops, and check the tightness and appearance of the throat hoops at least once a quarter. When problems are found, deal with them in time to avoid small problems from turning into major failures.
4. Improve the use environment: Try to improve the use environment of the waterline to avoid the throat hoops being in a high temperature, high humidity, and corrosive environment for a long time. For example, for waterlines that are easily exposed to chemicals, protective measures can be taken, such as adding protective covers or performing special protective treatment on the throat hoops.