How does T-post hose clamp work? Detailed guide
How T-Pole Hose Clamps Work Among the numerous hose connections and fixing devices, T-Pole Hose Clamps play an important role…
How T-Pole Hose Clamps Work
Among the numerous hose connections and fixing devices, T-Pole Hose Clamps play an important role with their unique design and reliable performance. Understanding how T-Pole Hose Clamps work is essential for the proper use and maintenance of systems involving hose connections.

1. Structural composition
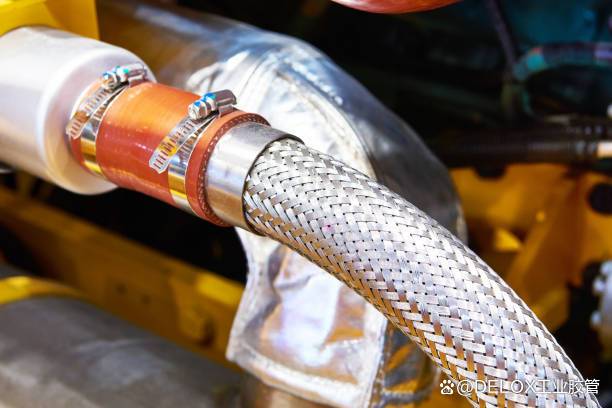
The T-column hose clamp is mainly composed of two parts: a metal strip with holes or slots and a T-bolt. The metal strip is usually made of high-strength and elastic materials such as stainless steel. This material selection ensures that the metal strip can maintain a stable shape when under pressure and can adapt to the slight deformation of the hose to a certain extent. The metal strip is ring-shaped, and its width and thickness are designed according to different application scenarios and load requirements in order to evenly distribute the pressure when clamping the hose.
The T-bolt is the key operating component of the hose clamp. Its T-shaped head design is convenient for rotating with tools, and the bolt rod cooperates with the hole or slot of the metal strip. The length and diameter of the T-bolt are also determined according to the overall specifications of the hose clamp to ensure that there is sufficient mechanical strength to generate the required clamping force during the tightening process.
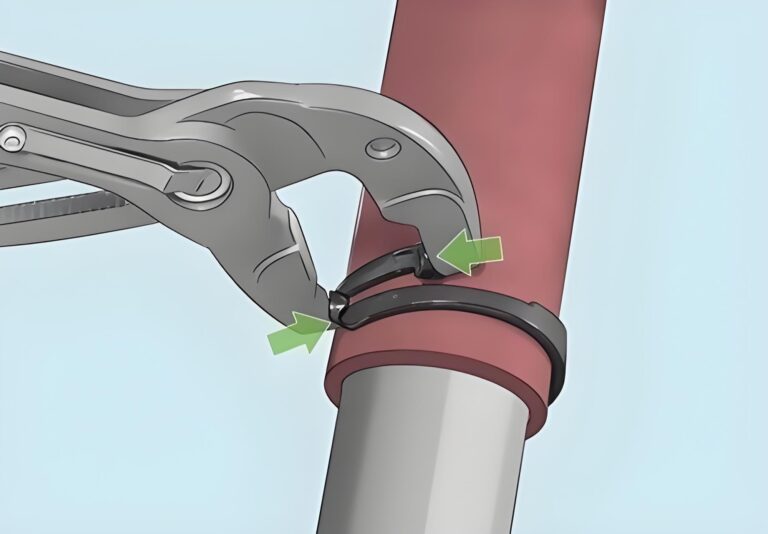
2. Installation process
When you need to use a T-column hose clamp to fix the hose, first wrap the metal band around the outer circumference of the hose. During the wrapping process, make sure that the overlapping parts of the two ends of the metal band are aligned, and that the holes or slots on the metal band for the T-bolts to pass through are in the appropriate position. This step may seem simple, but it is the basis for subsequent clamping operations. If the metal band is not wrapped flat or the hole position is not aligned, it may cause uneven clamping force or the T-bolt cannot be installed normally.

3. Clamping principle
After the metal band is properly wrapped around the hose, insert the T-bolt into the hole or groove of the metal band. Subsequently, use a wrench or other suitable tool to rotate the nut on the T-bolt. As the nut rotates, the T-bolt moves in its axial direction. Since the two ends of the metal band are restricted, this axial movement of the T-bolt forces the circumference of the metal band to gradually decrease. This reduction in circumference will produce a radial inward pressure on the hose, which is the clamping force.
The magnitude of this clamping force is directly related to the tightening degree of the T-bolt. Proper tightening can ensure that the hose is firmly fixed and prevent it from loosening or falling off due to vibration, pressure changes or other external forces during use. Moreover, since the metal band is wrapped around the circumference of the hose, the clamping force can be evenly distributed on the entire circumferential surface of the hose, thereby avoiding damage to the hose due to excessive local pressure, while also ensuring a good sealing effect.
4. Adapt to different working conditions
1.Hoses with different pipe diameters
The T-column hose clamp can be used for hoses of various pipe diameters. For hoses with smaller pipe diameters, relatively narrow and shorter metal strips and matching smaller T-bolts are used. In this case, the torque required to tighten the T-bolt is relatively small, but it can also generate sufficient clamping force to fix the hose.
For hoses with large pipe diameters, wider and longer metal strips and larger T-bolts are required. Since large-diameter hoses have a larger surface area, greater clamping force is required to ensure the stability of the connection. Therefore, when installing large-diameter hose clamps, it may be necessary to use a larger torque to rotate the T-bolt so that the metal strip is fully tightened to generate sufficient clamping force.

2.Expansion and contraction of hoses
In actual use, the hose may expand or contract due to factors such as changes in internal fluid temperature and pressure. The metal strip of the T-column hose clamp has a certain elasticity, and the metal strip can stretch or contract accordingly when the hose expands or contracts slightly. This elastic property enables the hose clamp to adapt to the size change of the hose while ensuring clamping, without damaging the hose due to excessive squeezing, and without loosening due to hose shrinkage.
In some application scenarios where the expansion and contraction of the hose are required to be high, designers will consider choosing a metal belt material with better elasticity or appropriately reserve a certain margin when selecting the model to ensure that the T-column hose clamp can maintain a good clamping effect and connection stability throughout the entire working process.
In summary, the T-column hose clamp effectively realizes the reliable fixation and connection of hoses of different diameters and working conditions through its ingenious structural design and working principle, providing stable protection for various systems involving hoses.

What does a T-post hose clamp look like?
The T-post hose clamp is mainly composed of two parts: a metal band with a groove and a T-bolt. The metal band is usually made of stainless steel or other suitable metal with a certain degree of elasticity and strength, and is in a ring shape that can be wrapped around the hose. The T-bolt is perpendicular to the metal band, and its head is T-shaped, which is convenient for operation with tools.
How is the T-post hose clamp installed on the hose?
When installing, first wrap the metal band around the outside of the hose to be fixed, so that the overlapping parts of the metal band are in the appropriate position, where there are holes or slots for the T-bolts to pass through. Then insert the T-bolts into these holes or slots, ready for subsequent tightening operations.

How does the T-post hose clamp generate clamping force?
After the T-bolt is inserted, the nut of the T-bolt is rotated by using a tool such as a wrench. As the nut rotates, the T-bolt moves in the axial direction. Due to the restrictions at both ends of the metal band, this movement of the T-bolt gradually reduces the circumference of the metal band, thereby generating a radial clamping force on the hose. This clamping force acts evenly on the circumference of the hose.
How does it ensure the stability of clamping?
On the one hand, the combination of T-bolt and nut can provide stable tension to keep the metal belt in a tightened state. In addition, the width and thickness of the metal belt are calculated in design to have enough contact area with the hose when clamping, dispersing the clamping force and avoiding damage or slippage of the hose due to excessive local pressure. At the same time, the thread design of the T-bolt and the matching of the nut can prevent loosening and ensure the continuous stability of the clamping force during use.
How does working on hoses of different diameters differ?
A: For hoses of different diameters, you need to choose the right size T-post hose clamp. If the diameter is small, a narrower and shorter metal band and a T-bolt of the corresponding specification will be used; for large diameter hoses, a wider and longer metal band and a T-bolt of the right size are required. During operation, large diameter hoses may require more torque to fully tighten the metal band to achieve the appropriate clamping force, but the principle is to clamp the hose through the cooperation of the T-bolt and the metal band.

How does the T-column hose clamp adapt to the expansion and contraction of the hose during operation?
Since the metal belt has a certain elasticity, when the hose expands or contracts due to factors such as temperature changes and internal pressure changes, the metal belt can stretch or contract accordingly within a certain range. This elasticity can ensure clamping while not causing excessive squeezing or loosening due to slight changes in the size of the hose, thereby maintaining a good connection state. If there is a large expansion and contraction, you can consider reserving a certain margin or choosing a metal belt material with better elasticity when designing and selecting.